Introduction |
· Next To Punjab, Western Part Of Uttar Pradesh Rich In Natural Heritage Is Considered To Be The Major Contributor To The Food Bowl Of The Country. However, Linear Growth In Population And Unplanned Colonization Lead To Rapid Fragmentation Of Land Holdings And Shrinkage In Fertile Cultivated Areas. |
· Due To Declining Profitability The Farmers Are Considering Farming As A Secondary Occupation Which Resulted Large Scale Migration Of Rural Mass To The Nearby Towns And Cities. In India, More Than 70 Percent Of The Total Population Of The Country Still Live In Villages And Mainly Depend On Agriculture And/Or Related Enterprises. |
· Marginal And Small Farmers Constitute More Than 84 Percent Of The 115 Million Operational Holdings In India Which Are Cultivating Only 29 Percent Of The Arable Land. Most Of Them Are Resource Poor And Work In Diverse, Risk Prone Environment. Further, Small Farm Holders Remained Deprived Of Benefits Of Advancement In The Field Of Agriculture, Major Beneficiary Being Resourceful Well Endowed Farmers. The Livelihoods Of The Small And Marginal House Hold Families Are The Major Concern. |
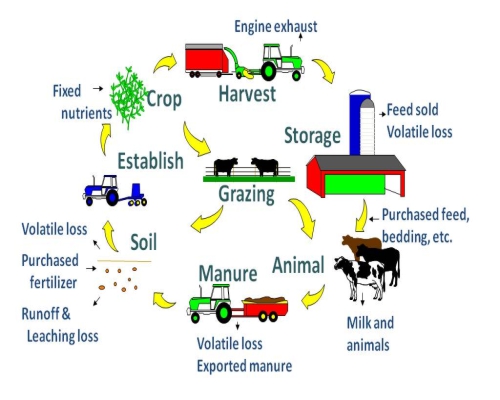
· The Improper Tapping Of The Potentialities Of Each Component In The System Make The System Unviable. Different Farming Systems Have Been Evolved Independently And Being Practiced By The Farmers Without Any Rationale For Utilizing The Wastes And Residues Arising Out Of Cropping/Animals And Other Associated Enterprises At Farm Resulting Wastage Of Resources. The Income From Average Farmers From Cropping Alone Is Hardly Sufficient To Sustain His Family. |
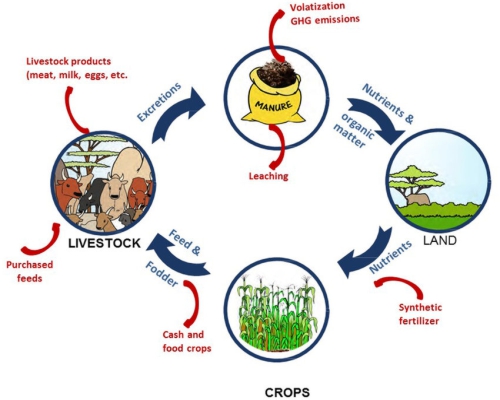
· Dairy, Irrespective Of Kind Of Animals And Their Breeds, Has Been An Integral Part Of Prevailing Farming Systems Across The Country. On Farm – Farming Systems’ Characterization Survey Of The Country As A Whole And Western Plain Zone Of Uttar Pradesh Conducted By The Project Directorate Revealed That There Is Either Stagnation Or Reduction In Productivity And Profitability Of The Important Crops. The Income From The Livestock Remained Fluctuating And Also Uncertain. |
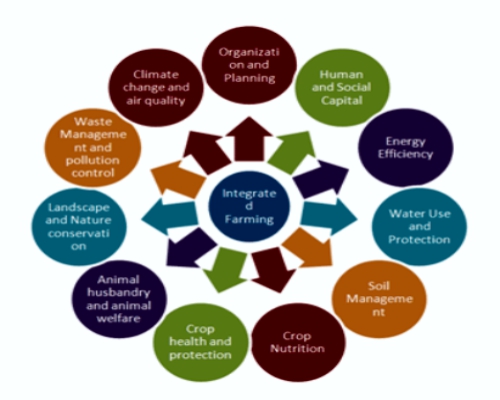
· Infertility In Cows And Buffaloes And Large Scale Mortality In Poultry And Goats Are Some Of The Major Problems Identified For Such Uncertainty. Because Of Poverty, The Small Land Holders Are Reluctant To Adopt New Technologies And/ Or Enterprises. Farming System Is A Resource Management Strategy To Achieve Economic And Sustained Production To Meet Diverse Requirements Of Farm Households While Preserving Resource Base And Maintaining A High Level Environmental Quality (Lal And Millu, 1990). |
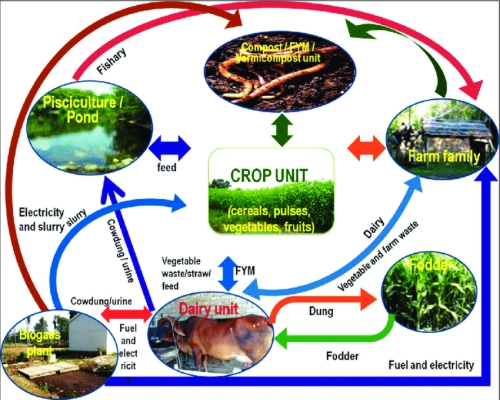
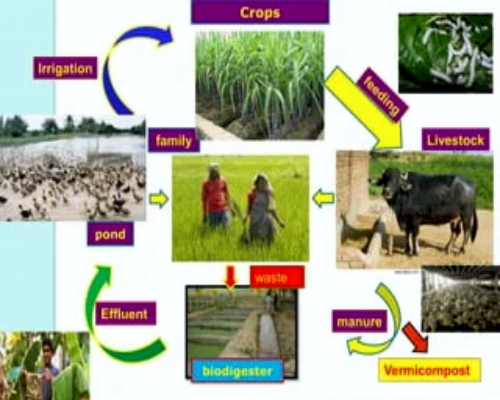
· Integrated Farming System Models Developed In Different Parts Of The Country Involving Dairy, Duckery, Poultry , Horticulture, Apiary, Pisciculture And Plantation Crops Viz; Coconut, , Cocoa, Nutmeg, Banana, Pineapple Etc. Along With Crops, Have Been Found To Increase Net Profit Significantly As Compared To Cropping Alone. |
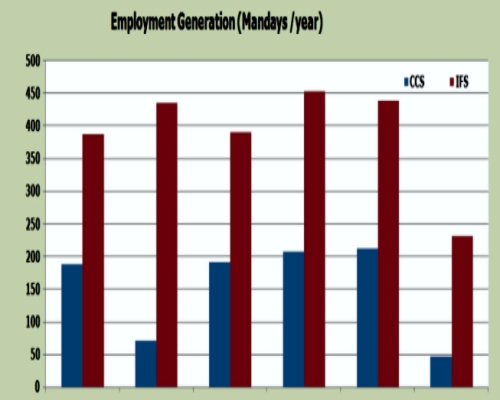
· These Ifs Systems Were Also Found More Sustainable And Employment Generative. Balasamy Et Al (2003) Obtain Net Profit Increase From Rs.22971/Ha/Annum In Rice Alone To Rs.31788/Ha/Annum In Rice + Fish + Azolla. In Telangana Zone Of Andhra Pradesh, The Major Crops Grown Are Rice, Maize, Jowar, Groundnut, Sugarcane And Cotton And Other Components Include Buffalo, Goat, Sheep And Poultry. The Results Of A Study (Radha Et Al; 2000), Conducted On Survey Based With Three Agricultural And Livestock Based Farming Systems Viz., Dairy, Poultry And Sheep Rearing Clearly Revealed That All The Farming System Generated More Than 3 Times Additional Employment Over Arable Farming . |
· The Net Returns Were Higher In Agriculture + Dairy (Rs.35293) Followed By Agriculture + Poultry (Rs.26830) And Agriculture + Sheep Rearing (Rs.14665). Among Different Farming Systems, The Agriculture + Dairy Was Proved To Be More Promising Than Others. The Main Reason For High Return That Stover Of Maize/Jowar For Fodder And Their Grains For Feed As Well As Sugarcane Crops To Feed Cattle Buffalo Were Available At The Farm. |
· Ifs Studies Conducted On Farmers Fields In Punjab Conditions, Gross Profit Was Found To Increase From Rs.81200/Ha/Annum In Cropping (Rice-Wheat) Alone To Rs.154000/Ha/Annum In Crop+Dairy And Rs.113200/- In Fish+Piggery System Of Farming (Gill,M.S.,2004). Encouraging Results Of Ifs Approach In Uttar Pradesh Has Also Been Reported By Gurbachan Singh (2004) And Singh Et.Al.(2007). |
· Keeping In View The Importance Of Integrated Farming Systems In Substantial Increase In Profitability Of Households An Attempt Was Made To Integrate Best Possible Enterprises To Study The Feasibility And Develop Appropriate Model For Western Plain Zone Of Utter Pradesh. The Results Obtained During The Period Of Study (2004-2010) Are Discussed Here For Ready Reference Of Researchers, Planners And Farmers. |